Game Intelligence - Soccer Elite Players Have It, How to Get It
One of the classic myths about sport is that elite athletes are brawny hulks of muscle with poor intelligence and low IQ, that have any strategic thinking processes sweated out of them at mindless training sessions. However new research has shown that elite soccer (football) players have superior 'game intelligence' that involves problem solving, making quick decisions, creativity and developing strategies. In this article I discuss the concept of Game Intelligence and review the research that have been conducted in Soccer and other games. I will also examine how it is revolutionising the training and selection of future soccer players.
- So what is game intelligence?
- Is it real?
- Do elite athletes have it?
- How is it developed?
- How can coaches develop it amongst their players?
- How do you test for it and find athletes that show potential for developing game intelligence?
- Does it apply in other games and sports?

So what is game intelligence? Is It Real? Do Elite Athletes Have it?
Despite current attitudes, game intelligence is fundamental to the way players make decisions in sport, especially team games.
Game intelligence is an ability to rapidly process information, apply rules and strategies, and making sound independent on-field decisions.
In soccer, every position and every situation, requires a specific type of intelligence - some of this is derived from experience, but some of it depends on innovation and creative abilities which are innate and can be developed.
The game intelligence skills needed by a goalkeeper are different from those required by a forward or central defender. Each position has a different set of problems to be resolved, but the mental skills and game intelligence capabilities are similar - they are simply applied in different ways.
The intelligence of a player, their experience, their physical ability and agility are the driving force for team success and individual performance. Quite often, two player with similar physical abilities and experience, will perform differently because of differences in being able to reading the game, and make quick and strategic decisions.
A good team player must be able to quickly adapt, change strategy, make good decisions for the right reasons and keep negative responses and outcomes to a minimum.
Game intelligence in sports, often referred to as executive functions, does not correlate with general IQ scores, but research has shown that successful soccer players have enhanced mental creativity and strategic decision-making. Success in ball-sports also depends on how information is processed and decisions made as well a technical skills.
This enhanced ability and performance relates to attributes such as pattern recognition, visual and mental anticipation and knowing what matters when faced with strategic decisions.
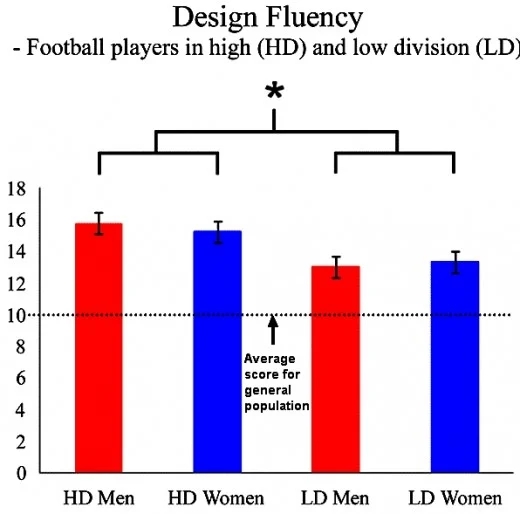
A group of European sports science researchers recently conducted a study to measure decision making abilities of a range of soccer players from various soccer divisions. The researchers measured game intelligence using a test procedure known as D-KEFS, which assesses skills in creativity, problem solving and rule making (see below for details).
The highest scores were achieved by players in the Sweden’s most elite soccer league, followed by players from a lower division. A group of people from the general public showed scores below both groups of soccer players.
The results for the Elite group of soccer players was in the top 2 % of the scores when compared with the general population.
This study has been published:
"Executive Functions Predict the Success of Top-Soccer Players"
As shown below the scores were significantly higher for Elite soccer players than those in standard grades. Soccer players scored higher than a group of subjects who were non-players.
This implies that the skills to do well at the test are improved by playing soccer, but it also implies that players are successful and reach the Elite teams because they have innate abilities which are developed through experience playing soccer. It would be interesting to compare the results for young people who play a lot of online games.
The executive functions are important as successful players must constantly re-assess the game situation and player positions, use past experiences for similar situations, create new possibilities, make quick decisions for actions, but also quickly eliminate bad decision options.
The researchers concluded that the process for selecting future stars should not only include assessment of physical capacity, ball control, stamina and general soccer skills and performance, but also assess executive functions using tests applied in this study.

How is it developed?
Executive function capability (game intelligence) is considered to develop throughout childhood and the teenage years, from about 3 year up to 19 years of age.
Each epoch of soccer training was characterized by certain fashions and trends. In the 50's and 60's when soccer coaching started, it was mostly focused on improving technical skills. In the 70's and 80's the focus was mostly on the physical conditioning of soccer players. Today there is a greater emphasis on mental abilities, strategic thinking and decision making as well. Part of this is experience, but it is something than can be learnt and certain players have more ability that others in game intelligence. Elite players get to be elite because they have developed these skills and it shows.
There is a need for systematic development of tactical awareness, decision making and thinking about the flow of the game from a very early age. This can be done during training by employing simplified games and drills to develop tactical experiences and decision making, with coaches providing feed-back and guidance. One method is to develop drills where players are exposed to simplified games such as 3 v 1 players, 2 v 1 players and 3 v 2 players. Each player has to face and resolve a series of problems to cope with these situations.
Skills such as good perception, looking at the big-picture are required for a correct assessment of the game situation and what to do. These skills can be taught and practiced, especially using game reviews and coaching videos.
How can coaches assess and develop it amongst their players?
Modern coaches must be prepared to modify their coaching style to stimulate game intelligence. To get more players on the pitch who can think for themselves, coaches need to stimulate more game intelligence and instruct less. Instead of being hands-on instructors on the soccer side-line, they should become guides, consultants, leaders and organizers of information and assessing the fostering strategic thinking.
To develop game intelligence in soccer players a coach should teach players to:
- draw on past experiences (including videos) when face with a given situation to quickly and efficiently help players make strategic decisions. This involves teaching players what to look for and the signs of opportunities that the payers an exploit and develop
- read the game and each situation to understand what is happening on the pitch which requires perception, experience, knowledge and the ability to recall past situations and their solutions
- teach players that part of being an intelligent player is to anticipate how the situation is likely to develop and where it is heading. The ability to anticipate depends on good perception, the ability to visualize the situation and how various decisions will affect the outcome.
- get players to realise that just like the technical skills, no player is born with an innate high-level of game intelligence in soccer, but many have the instincts and prerequisites to learn quickly. To develop their natural inherited potential fully, players must be prepared to undertake a varied range of activities and simplified games. Development of game intelligence is part of training similar to stamina and technical training.
How to test for the potential for developing game intelligence
The signs of game intelligence potential coaches should look for during games and coaching sessions are Players who
- are fast thinkers - generally choosing the best option quickly
- can quickly prioritise and rank all the various alternatives and assess their relative merits and risks - such players can recall the processes they used to make decisions during after-game analysis
- knows the limitations of their own abilities and those of the team so they choose the best option not the impossible one.
- are never rushed and appears confident and assured when conducting a particular move on the pitch. Such players take time to take in what's occurring and always appears to have time to make the best decision. Such players also now the dangers of rushing things - but how to exploit the situation with a split-second decision.
- always appears to balance risks, rewards and challenges so that the negative outcomes are minimized. The player is brave enough to take risks - go ALL IN, but not stupid enough to risk everything on unlikely moves.
- show that they can adapt to changing situations in the game.
- know that move may not always come off, but is self-confident enough to make many great decisions to offset a few mistakes that they recognise and take responsibilities for
- knows what he is going to do with the ball before even receiving it.
- uses his creativity, skill and strategy for the benefit of his teammates and team performance.
- knows how to move into open spaces to create opportunities.
- frequently asks questions and quickly adapts to the advice given and learns from mistakes.
- has the ability to memorize a large number of plays and can adapt them to he situation.
- has the self-confidence and ability not to let their game be affected by stress, but know how to use it to advantage. These players make good contributions in decisive matches and in stressful situations. Pressure and stress can nullify the usual intelligent play or some players.