Q&A How Does Twisted Pair Cabling Stop Interference?
Have you ever wondered why most of the wires in a communication cables are Twisted?
Why should such a simple thing make a difference?
The reason why is a fascinating story with an interesting history.
Conveying information in wires
- A message is converted into a code that can be communicated via a change in voltage or current.
- The message is sent along the wire to the recipient who will decode the message.
- Decoding digital signal is based on a very strict difference in voltage (amplitude). 1’s and 0’s (binary).
- Early telegraph systems used Morse Code and were coded and decoded by humans who knew the ‘language’. Nowadays computers code and decode the messages based on specific protocols.

Electromagnetic Interference
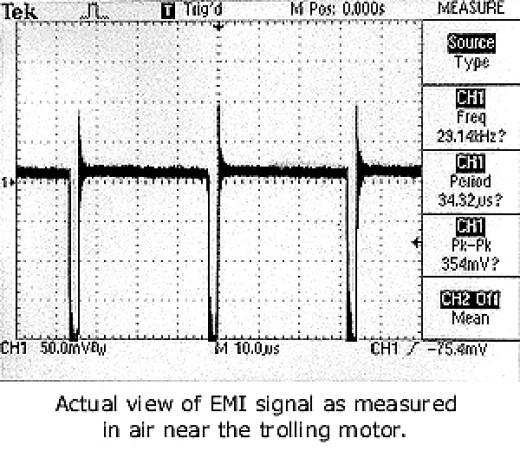
- EMI (or simply ‘noise’) is a disturbance that effects an electrical circuit, it may obstruct, interrupt or otherwise degrade the performance of the circuit.
- In wire communication it degrades the signals (interferes with the waves) as they travel along the wire meaning that a computer will be unable to understand the decoded signal (due to the strict voltages) and the message will need to be resent.
- EMI is caused by stray electromagnetic waves moving through the circuit.
- Electromagnetic waves are unavoidable because they are emitted by everything in the Universe but the effect of EMI on a wire can be lessened in several ways.
How Do You Reduce EMI?
- Stay away from places that produce large amounts of noise, i.e. Factories, Trains, Big Speakers, etc. Not really practical.
- Use a faraday cage, place grounded metal around the wire that will transport the signal. It stops EMI but it is very expensive, not flexible, etc.
- Use Differential signalling, this uses two wires close to each other, both send the message at the same time, but one sends an inverted copy. Noise degrades the signals normally. The receiver inverts one of the signals and adds the two signals together. This “cancels out” the noise doubles the strength of the signal you care about. However, having a source of noise closer to one wire in the pair than the other for the span of the wire will wreck the signal, this is called crosstalk and is experienced when lots of wires are bundled together.
History
- Telegraph lines and early telephone lines used a single wire to send a signal.
- When trams were brought in the sparks and current changes created a lot of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- To get around this telephone companies created differential mode transmission. And used two wires about a metre apart.
- When AC electrical power lines were run along the same poles a new source of interference was created - crosstalk. They got around this problem by crossing the wires every few poles. This eliminated the low frequency noise.
- When telephone wires were bundled together the wires had to be twisted a few times an inch rather than a few times a mile. This is because the crosstalk was of a higher frequency.
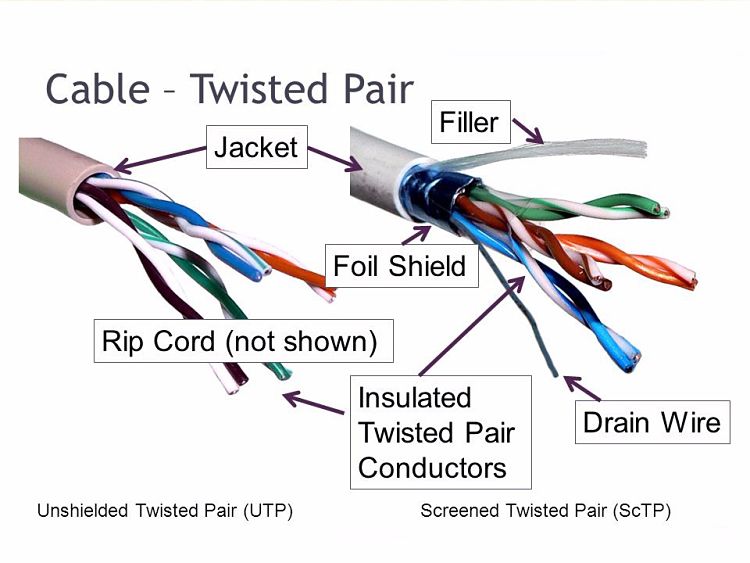
The Twisted Pair
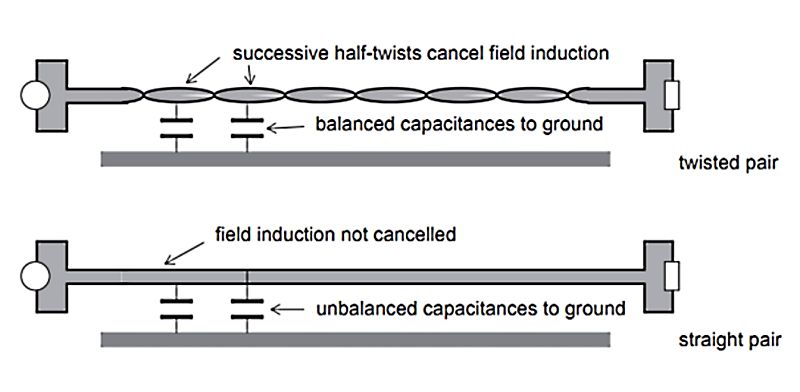
- The solution to this is twisting the pairs! This means that any noise created through crosstalk on one of the lines, is also created on the other line in the next ‘twist’.
- The pairs are twisted pretty often, a couple of times every inch, the twisting must be consistent for it to work properly.
- Different pairs touching each other can’t have the same amount of twists per inch or there will be consistent crosstalk across the lines.
- This creates the cheapest possible way to reduce EMI on a wire. This makes communication more efficient because less of the message needs to be retransmitted.
Note:
The shielding will be influenced by external EMI signals but has the same affect as you've stated: an induced voltage will move electrons in the shielded portion, thus removing the electric field issue on the conductor, while the magnetic field will be greatly attenuated by means of opposite currents induced into the conductor by the offending source and the shield, itself. A twisted pair, from this point, may or may not assist in EMI reduction but it all comes down to how the ground is shielded.
Many folks get confused and think that the shielding acts like a physical barrier that electromagnetic waves bounce off of when really the external signal is cutting through the shielding and the wires all at once, it's just opposite forces are created and thus, cancel each other out.