Use Intermittent Fasting & Exercise to Create a Calorie Deficit, Lose Weight
Most people throughout the world consume more calories than they need to maintain their weight each day. When a person consistently eats more calories than their body needs at rest, and for calories burned in exercising, the extra calories eaten are stored as fat.
There is widespread evidence that the introduction of highly processed foods in the 1970's, based on white flour, white rice with added sugar led to people passively overeat, and consume far too many calories. So that even when people had a so-called healthy diet or 3 meals a day without junk foods or sugary foods and drinks they still consumed far too many calories. The reason is obvious - their meals had been enriched because of the consumption of processed foods such as breakfast cereal, breads and prepared meals.
Various studies have shown that this enrichment amounted to an average of 500-700 extra calories. This is equivalent to an extra meal compared with a pre-1970's average daily consumption of around 2000 Calories per day.
Importantly this extra calorie was passive, that is it was caused by the calorie enrichment of standard size meals and a standard or 3 meals a day. Added to this is data which shows that meal sizes and portion sizes have increased. Eating junk foods has added to the strong rise in daily food consumption. This is active overeating to boosted calorie consumption to excessive levels.
The impact of processed foods on excessively high daily calorie counts can be reduced in several ways:
Eating only raw or unprocessed foods such as fresh vegetables, whole grains and eliminating bread, white rice, white flour and products such as pasta and baked goods.
Reducing portion sizes or Only Eating The Better Half. Reducing meal sizes to 3/4 or 1/2 will bring the calorie counts of 3 standard meals a day back into an acceptable range that will sustain body weights rather than causing weight increases.
Intermittent Fasting on a daily or weekly basis, can reduce calorie intakes. 'Don't Eat Lunch' or other strategies for only eating 2 meals a day will bring the daily calorie counts back into an acceptable range. Likewise, fasting for 1 or 2 days a week will reduce calorie intake.
What is Fasting
Fasting is defined as a period or time when food consumption is partially or total restricted. It can be applied for selected foods or all foods entirely, and does not apply to water consumption. The known health benefits of fasting, based on people who fast for religious reasons, include: decreased blood pressure, decreased resting heart rate, improved heart health and function, increased insulin sensitivity, reduced cholesterol, and reduced inflammation.
Fasting may be undertaken for general health or well-being. It can also be adopted for dieting or weight loss programs, or more commonly for religious reasons. The American Heart Association in reviewing various research studies has concluded that regular fasting is associated with lower rates of heart failure and improved metabolism. Fasting could potentially be the key to achieving a long, happy and healthy life. It is the foundation of the 'Stay Hungry' movement. Many studies have shown that people who fast regularly have an almost 45% lower mortality rate compared to those who don’t fast.
What are the Various Types of Fasting?
For fasting health benefits, intermittent fasting has the best outcome in terms of temporary or ongoing health benefits, long term fasting is akin to starvation and can be very unhealthy.
Different Approaches to Intermittent Fasting Programs and Timetables
Twice a week method (5:2)
Restrict daily calories to about 500 a day for two days a week (for example over the weekend).
Other days, eat a healthy diet (2000 calories)
Alternate day fasting
This involves fasting every second day.
Restrict calorie consumption on fasting days to about 500 calories (about 25% of the usual intake).
Other day, eat a healthy diet (about 2000 calories)
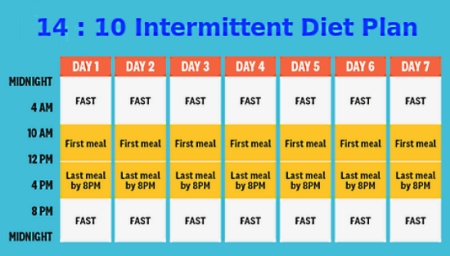
Within a Day - Time-restricted 16 hour fasting
Fast completely for 16 hours a day, for example between bedtime and 11.00 a.m. hours on the next day
Eat only during an eight hour period.
One may eat between 11.00 a.m. and 7:00 p.m.
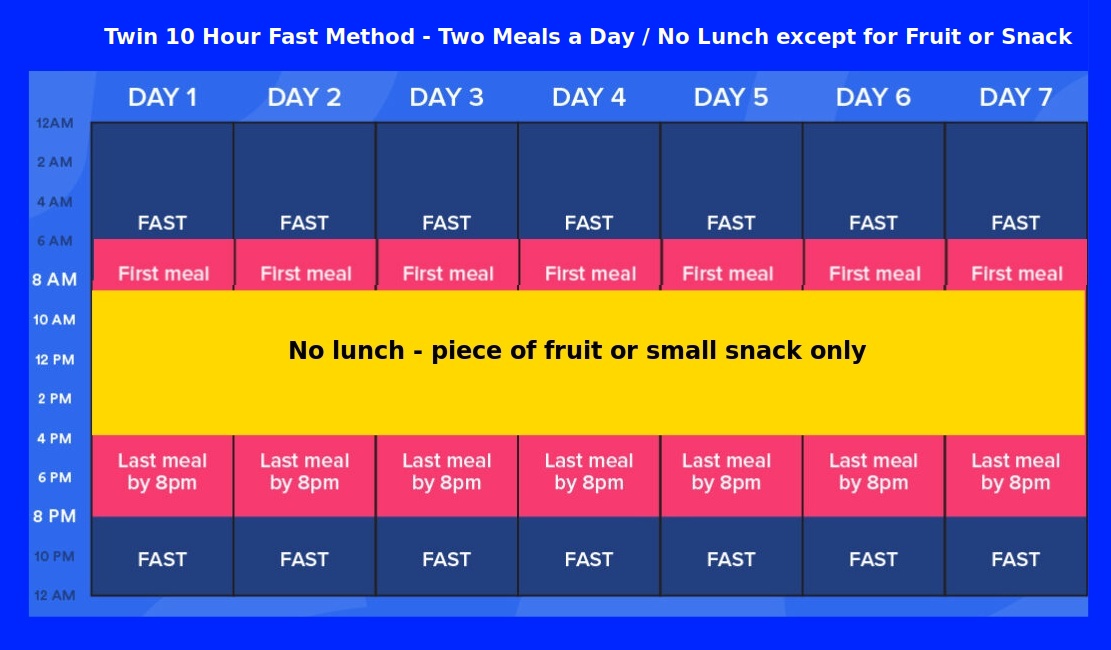
Within a Day - Time-restricted Twin 8 hour fasting
Fast for 16 hours a day in two 8 hours periods, overnight and between breakfast and dinner/ supper (Don't eat lunch or snacks)
One may eat breakfast and dinner, no lunch apart from a piece of fruit or small snack.
The 24-hour fast: Fast completely for one or more days a week
This method is not recommended as it can may cause extreme fatigue, dehydration, headaches, irritability and low energy.
What are the risks associated with fasting?
Be aware that fasting is not for everybody, especially for people with pre-existing health issues. Consult your doctor if any any doubt of the potential risks for you.


How Can These Ideas be Used for a Weight Loss Program
So how do you get rid of extra fat you've gained because of overeating and the impact of calorie enriched processed foods and lose weight? The simply answer is to apply the calorie intake reduction to the point that you create a Calorie Deficit. What this means is that you eat far fewer calories than your body burns in maintaining itself at rest and the extra calories burned through exercise.
Formula: Calorie Deficit = Calories Burned - Calories Eaten
The higher the deficit - that is the more negative it is, the faster you will lose weight.
Try this App >CalDef - Tracker WebApp - The Calorie Deficit Path to Weight Loss
- 1 kg of body fat is equivalent to 7500 calories
- 1 lb of body fat is equivalent to 3410 calories
So to lose 1 kg of body fat you need to create a calorie deficit of 7500 calories. This is equivalent to and extra 1100 calories burned, or not eaten each day over 1 week.
To lose 1 lb of body fat you need to create a calorie deficit of 3410 calories. This is equivalent to and extra 500 calories burned, or not eaten each day over 1 week.
There is a simple principle here. When you create a calorie deficit, your body must get the energy it need to maintain itself, from stored fat. This means that some of the fat that you carry on your thighs, hips or around your waist, is broken down to yield the calories your body needs.
It is also clear that you can create a calorie deficit by changing the exercise component of the calorie deficit equation. If you exercise more often and for longer each day, without changing the amount of food consumed, you can generate a deficit by burning extra calories.
However, this is much harder to do, because contrary to what most people understand, exercise burns relatively few calories. Which is harder - skipping lunch (600 Cal) or walking 10,000 steps, running for half an hour, swimming or bicycling for an hour.
A summary of calories expended for a range of exercises is provided below:
- Walk 1 hour => 350 Cal
- Walk 1,000 steps => 60 Cal
- Walk10,000 steps => 600 Cal
- Run 1 mile at average speed => 100 Cal
- Run 1 km at average speed => 60 Cal
- Run 5 miles at average speed => 500 Cal
- Run 5 km at average speed => 300 Cal
- Swim 1 hour => 500 Cal (slow pace), 750 Cal (fast pace)
- Swim one lap (50 m pool) => 25 Cal (slow), 50 Cal(fast)
- Gym workout for 1 hour => 200 Cal (light), 350 Cal (medium), 500 Cal (heavy)
- Bike Ride for 1 hour at 13 miles/hour (20 km/hour) => 600 Cal
- Bike Ride for 1 hour at 16 miles/hour (25 km/hour) => 740 Cal
The best strategy to create a calorie deficit each day or week is to use a combination of eating less, and burning more, calories.
There are several great WebApp tools available for estimating your calorie deficit:
Calorie Deficit Calculator for Males and Females
This tool calculates your Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) - that is the calories you burn at rest during the day. The formula is different for males and females. The rate depends on your body size - weight and height. It also depends on your age and activity level. Younger people tend to be more active. The App calculates your calorie deficit using the calories eaten each day in food and calories burned through extra exercise. This tool can be used to show you whether you have a calorie deficit and how to increase it so that you lose more weight each day of week
Combined Weight Loss Tracker and Calorie Deficit Calculator
This App combines a Weight Loss Tracker with a Calorie Deficit Calculator.
You start by Entering your Set Up Information => your sex, age height, start weight and loss rate as kg or lb per week.
The tool predicts your target weight for each day of your program after the start date using the loss rate you specified. Your target weight for the day is your initial weight less the number of days elapsed times the daily loss rate. Using this, it helps you keep your weight loss on track to meet your goal.
To help you meet this target the App included a Calorie Deficit Calculator.
The tool calculates your calorie deficit by estimating your Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) from your sex, age, weight and height. Your RMR is the calories you burn at rest during the day without exercising.
Each day you enter the calories consumed in food and the calories burned through exercise. Quick guides are provided to help you estimate calories in various meals.
Food
- Average general Calorie intake => 2000-2500 Cal
- Calories for 3 small meals => 1800 Cal
- Calories for 2 small meals => 1000 Cal
- Muesli with 1 cup of milk => 500 Cal
- Fish 400 g with salad => 600 Cal
- Steak 300 g with salad => 800 Cal
- Apple, orange or banana => 100 Cal
Deficit Required to Lose Weight
- You need 7,800 calorie in deficit to lose 1 kg
- Deficit of 1,100 per day => 1 kg loss per week
- Daily loss for 2 kg per week is 0.3 per day
- 1 kg of fat equivalent to 7500 calories
- The tool estimates your daily calorie deficit.
You may need to adjust the deficit to keep on track to meet your goal weight over time.
If you fall behind the loss rate you specified, you will need to eat less or exercise more (very simple).
Of course the essential element missing is DISCIPLINE!
Summary
So to sum up - How do you create a deficit of 500 calories per day or 3500 calories per week? There are three healthy ways to create a calorie deficit for effective long term weight loss.
Eat Less Food - If you reduce your portion sizes, meal sizes, eliminate snacking and choose reduced-calorie foods at mealtime, you will consume fewer calories each day. You can achieve the same thing via intermittent fasting - skipping one meal per day (Don't Eat Lunch). If you reduce your caloric consumption enough, you will create a calorie deficit large enough for weight loss.
Get Active - The total number of calories your body requires each day depends on your activity level. This includes your general physical movement. Calories are burned to sustain your general metabolism and to maintain your body temperature and other functions. It also includes the extra exercise you may do every day. If you increase the number of calories your body burns in a day, but still eat the same number of calories in food, you will reach a calorie deficit, burn fat and lose weight.
Combine Changes in Diet, Calories Consumed and Exercise - Most successful dieters use a combination of increased exercise and dieting to lose weight. For example, they may eat 250 fewer calories each day. Also they may take a brisk walk for one hour to burn an additional 250 calories. The calorie deficit in this case would be a total of 500 calories for the day and a 3500 calorie deficit each week. This would mean a weight loss of 1 lb per week or 1 kg per fortnight.
The advantage of the WebApp is that it tracks your weight loss compared with your target and calorie deficit at the same time. So, you can see if your strategy is working. You may need to adjust the size of the calorie deficit to keep ON TRACK. This can be rather brutal if you fall behind significantly.
The same system can be used to develop a weight maintenance program by developing a diet and exercise program that keeps your weight within your target range.