Q&A Which Cooking Methods Retain Most Water and Fat Soluble Vitamins?
Many vitamins such as Vitamin C, are destroyed by heat and their benefits are lost. This means that cooking fruits, vegetables and meats will progressively mean that the level of such vulnerable vitamins in the food dishes will decline.
However, surprisingly eating raw foods does not necessarily mean that all the potential vitamins in the fruits and vegetables will be available.
Studies have shown that people who ate a raw food diet had below average levels of plasma lycopene which is a bright red carotene and phytochemical found in tomatoes, red bell peppers, watermelons.
Cooking breaks up the thick cell walls of many plants, so that the nutrients inside can be utilised. Many cells in raw food remain intact and pass through the digestive system without releasing their vitamin bounties for absorption.
Foods rich in fiber may pass through the gut partially undigested.
Other studies have shown that cooking changes the chemical structure of lycopene so that it is more available to be ingested from food.
When the 'linear' lycopene molecules in tomatoes are heated with fat during cooking the molecules are changed to a bent form that is more easily transported into the bloodstream and tissue in the body.
Cooking can enhance the availability of other vitamins as well. To cook or not to cook - that is the question and which cooking method retains the most vitamins.

Key Facts About the Loss of Vitamins in Food through Cooking
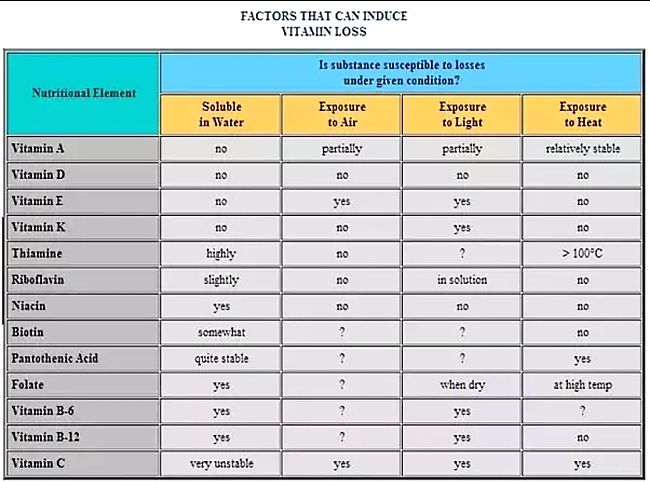
► Water soluble vitamins are more susceptible to cooking and canning processes.
► Canned carrots and peas lose about 90% of their natural Vitamin C.
► Frozen dark cherries have been shown to lose 50% of anthocyanins (an antioxidant associated with their red color) after six months.
► Cooking removes about 70% of the vitamin C in fresh spinach and general loses for other foods range from 15-55% depending on the methods and how long the food is cooked.
► Fat-soluble compounds like vitamins A, D, E and K and the carotenoids generally are retained better when cooked than the water soluble ones.
► A research study reached the following conclusions:
- Boiling retained more vitamins in vegetables such as carrots, zucchini and broccoli than steaming.
- Frying was by far the worst method for preserving nutrients when cooking.
► Cooking in the Microwave and in Pressure Cookers retained the most Vitamin C.
► The results from a research study conducted in 2007 found the following for retention of Vitamin C:
- 90% retained for Microwaved and Pressure-cooked vegetables
- 70-80% retained for Steamed and Boiled vegetables.
Benefits of Microwave Cooking of Vegetables for Retention of Vitamins
► Food is cooked quickly with no added water than can wash nutrients out of food.
► Reheated cooked foods generally lose no nutrients when reheated. You are less likely to overcook foods.
Examples:
- Broccoli and cabbage lose about 15% of Vitamin C when microwaved compared with 25-65% when boiled in water.
- Very little folate is lost in spinach when microwaved spinach compared to 20-25% lost when boiled.
Benefits of Steaming Vegetables for Retention of Vitamins
► Cooking times are relatively short
► Very little added water is used.
Examples:
- Generally nutrient loss is only 50% of that for Boiling.
- Carrots lose 15-30% of their Vitamin C when steamed
Benefits of Boiling Vegetables for Retention of Vitamins
► Boiling is generally considered the second worst method for cooking vegetables because the items tend to be cooked for a long time and are often over cooked. Frying is the worst
► Many vitamins and other nutrients are dissolved into the water and are poured down the sink when the cooked vegetables are drained.
► Nutrient loss varies a lot depending on cooking tines, the type of vegetable, whether or not the item is peeled and how finely it is chopped before being cooked.
Examples:
- Green beans lose about 45% of Vitamin C when boiled whole, but about 70% when French cut before boiling
- Broccoli loses about 35% of its Vitamin C after 11 minutes of boiling but only about 25% when boiled for 2-5 minutes
Tips for Preserving Nutrients when Boiling:
► Use little water
► Place food in water only when it's at full boil and cook for minimum time.
► Cover the pot, to speed up the cooking
► Re-use the cooking water soups and gravies
► Don't peel vegetables. Peeled potatoes lose about 25% of Vitamin C when boiled, but hardly any when not peeled.
Benefits of Roasting Vegetables for Retention of Vitamins
► Don't over-cook. The longer the cooking time and the higher the temperature, the more vitamins are lost.
► The lower the temperature the less quickly vitamins are destroyed
Examples:
- Beef cooked at 300 degrees F lost 30% of its thiamin, but 50% when cooked at 450 degrees F.
Benefits of Frying Vegetables for Retention of Vitamins
► Standard frying at very high temperatures causes the loss of most vitamins as the temperatures are far in excess of the boiling point of water.
► Frying is the worst method for cooking most vegetables.
► Very quick and very light stir-frying is better, but expect loss of many vitamins.
Examples:
- The loss of B Complex vitamins is 30-80% when fried, depending on the vegetable.
- The loss of Vitamin C from French fried potatoes can be as high as 90%.
Related Articles
=> Best Healthy Vegetable Chart - Calories, Fiber, Vitamins, Minerals
=> Do Your Really Need Vitamin and Mineral Dietary Supplements?
=> What Fruit is Healthiest For Calories, Fiber, Fat, Vitamins, Minerals
=> Avocado Nutrition Facts - Calories, Fat, Protein, Vitamins, Minerals
=> Q&A: Vitamin D Deficiency Rate Rising - Call for Adding Vitamin D to Food
=> Health Benefits Chlorella - Vitamins, Protein, Minerals, Nutrients
=> Vitamin D Deficiency - Health Problems, Symptoms, Treatments for Vitamin D Lack
=> Use Vitamin Supplements to Increase Memory and the Power of Concentration